If you are starting your business and people are not yet ready to buy your product, you then have not yet reach product market fit.
So what is product market fit? Product market fit is the level of match between what customers want and what a product provides. It is the value that in the business model that customers want and willing to pay for.
In this article, I will talk you through product market fit from first having an idea and then taking that idea, and turning it into something people are willing to pay for.
1. What Is Product Market Fit?
You know you have product market fit when when your product satisfies the market. This is measured by customers willing to purchase your product. Overall, it is the match between what customers want and what the product provides.
The purpose of product/market fit is to find a market where your product and your business will do well. This is searching for a viable market, and to establish a viable market you have to look for options that can then lead to growth. In turn, to establish you need to find the demand to justify which market option you would like to enter.
Marc Andersen describes product market fit as: “a means of being in a good market with a product that can satisfy that market.” He then goes to say “A lot of startups fail because they never get to Product /Market Fit”.
The aim for a startup in its very early stages should be to discover product/market fit. This is where the sustainable business model will be built up from. This means you are on a journey to discover what people want to pay for.
2. Marc Andreessen Talks About Product Market Fit
In the below passage Marc Andreessen talks about his experience when he finally discovers that his business reached product market fit.
“you can always feel Product/Market Fit when it’s happening. The customers are buying the product just as fast as you can make it — or usage is growing just as fast as you can add more servers. Money from customers is piling up in your company checking account. You’re hiring sales and customer support staff as fast as you can. Reporters are calling because they’ve heard about your hot new thing and they want to talk to you about it. The level of dedication and excitement by customers is an indicator of Product/Market Fit.”

Personal note – 2015, Kenya in a town called Kericho, I had my own business buying broken laptops and old computers and improving the specs. After I repaired these computers I then went out and sold them, my experience was just like Figure above. After the first month I had people ringing me every second from previous sales asking for more laptops and I simply couldn’t keep up with the demand.
3. Why is Product Market Fit Important?
Product market fit is important as it uncovers all the uncertainty in the market.
The start-up journey includes establishing the idea, creating prototypes that best resemble the idea (at minimal cost), take this prototype to customer and then get feedback. This process is repeated until people get excited and want to hand you their money for exchange of your product.
Marc Andreessen – You can always feel when Product/Market Fit isn’t happening. The customers aren’t quite getting value out of the product, word of mouth isn’t spreading, usage isn’t growing that fast, press reviews are kind of “blah”, the sales cycle takes too long, and lots of deals never close.
The customers are at the centre of every business so listening to the customer’s feedback and developing a product that can be scaled, and wanted by the masses is essential to predict market demands for future forecasts.
In a good market – a market with lots of real potential customers – the market pulls product out of the startup. The market needs to be fulfilled and the market will be fulfilled, by the first viable product that comes along.
Product Market Fit Leads to Growth
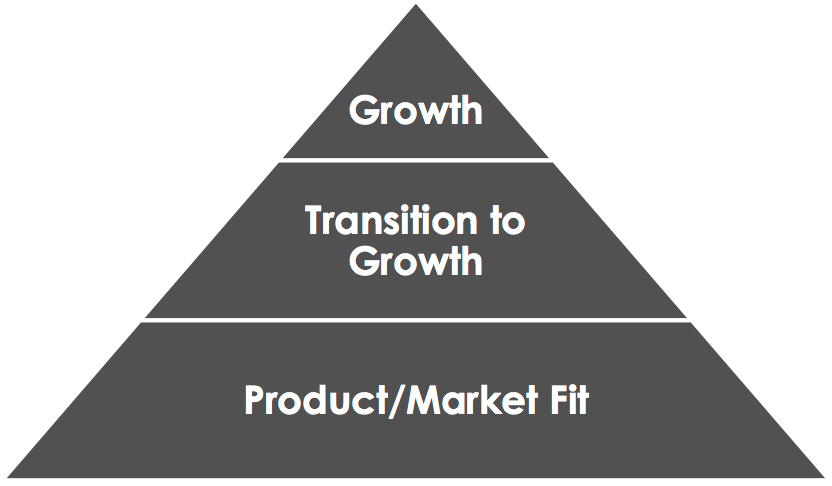
Overall, product market fit is the direct link to business growth and if a business is not growing then it is failing.
4. Myths About Product Market Fit
Ben Horowitz, co-founder of venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz wrote a blog post, ‘The Revenge of the Fat Guy’, in which Ben clearly busts the common myths about Product/Market Fit.

Sean Ellis, CEO and Founder of Qualaroo and GrowthHackers community – startups should measure their Product/Market Fit as soon as possible as it significantly impacts how one’s startup performs.
Andrew Chen – “Basically you want to get to the point where your product is working, and if you can’t get there within the first 1-2 years of your company’s existence, you generally run out of money or your team falls apart.”
Brian k Balfour – “My guess is most of you are screaming ‘when you reach Product/Market Fit!’ True, but knowing you have reached product/market fit typically isn’t a clean cut answer. It is a line that is always moving.”
5. Customer Development Process
Habving a good market means there is a decent volume of customers. This important because a lot of potential customers in a market will buy the first viable product that satisfies their need.
Generally in regards to the invention of the internet, applications are innovated to seek new audiences. Innovation in context of this application referred to changing processes to be more effective for a particular market. However, you could have a brilliant product with no market volume and that business would seize to exist.
There is not one way to achieve project/market fit but there are different tools that help manage the thinking process. Once the customer development process has been implemented and all the relevant information has been collected a test can be conducted whether the product is viable.
6. Minimal Viable Product
Before the full product is produced a minimal viable product is needed to ensure the product meets the customer’s satisfaction before big investments are made. Once released feedback is needed, listening to the customers, this can also be known as alpha and beta testing.
Marc Andreessen – The product doesn’t need to be great; it just has to basically work. And, the market doesn’t care how good the team is, as long as the team can produce that viable product. In short, customers are knocking down your door to get the product; the main goal is to actually answer the phone and respond to all the emails from people who want to buy.”
In addition people don’t care about how good the team is so long as they get the viable product. Blank (2012) has a similar approach as he says the customers are the center to every business and has created the below model is used find out about the market and search what it is the customers want.
7. Tools Used for Product Market Fit
Tools used to for product market fit are:
CV Plus
Before & After Canvas
8. CVPlus
The CV plus is a tool I used when developing businesses and it was used to outline what resources I have available. The resources include the assets, networks and skills you have available.
The most important thing to do at the start is to learn. In this learning process you need to start learning about.
- The business
- The entrepreneurs involved in the business
Try learning about the entrepreneur’s life and what skills they might have they could bring to your business idea or open opportunities for other ideas
- Skills
- Qualifications and education
- Work and experience And means of money making
- Resources/ assets
- Aspirations
- Contacts Networks
In the first stages of being effectual, it is useful to outline your resources and seek ideas that put your resources to use.
9. Before & After Canvas
This tool helps understand your chosen idea; to understand the problem and the impact of the solution it is helpful to imagine the hypothetical scene. It helps understand the current scene including competitors and shows how the new business idea will improve customer’s life. Always remembering the vision is just a series of guesses – this need to be turned into hard facts.
9.1 Before and after canvas
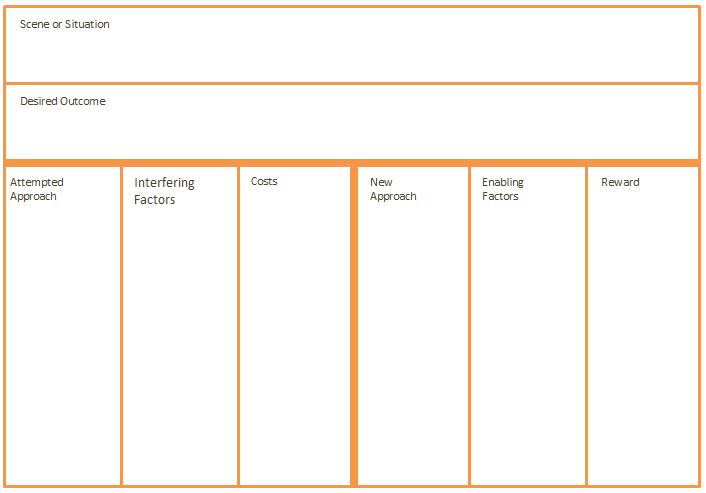
9. Structure of being a creativity entrepreneur
New Stimulus– Talking to new people and getting out of the building learning of problems and frustrations people have. Where there are problems lies opportunities.
Challenge your assumptions – Asking why? Challenge your assumptions.
Reframe the Question – try and discover what the customers actually want, not a faster horse but a car.
Connect and Combine – look at other industries how do they do it?
Attitude – Get the highest amount of volume of ideas, doesn’t matter how ridiculous as the best inventions was made from the most insane ideas and mistakes.
10. BMC
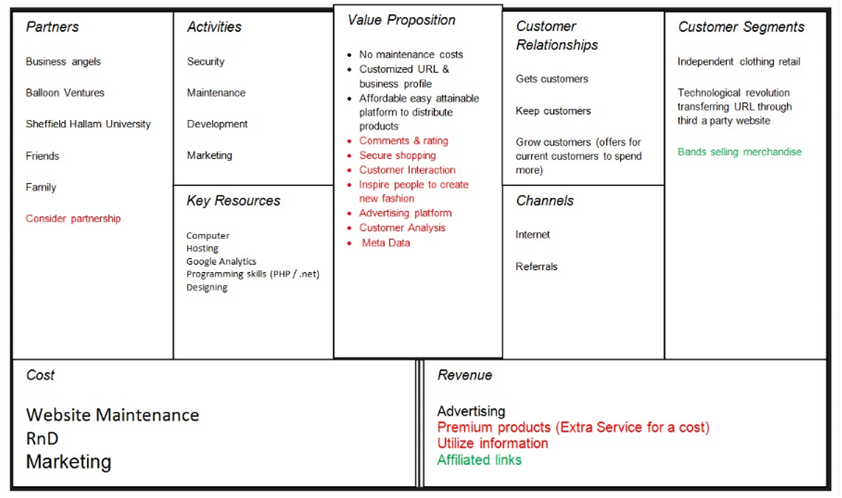
11. Customer Development Process
The business plan never survives first contact with customers so the customer development process is designed to correct this. This means the marketing and development team should spend at least 20% of their time out of the building understanding customer problems and needs.
The customer development process is building something to test your hypothesis against. IT is gaining real data acquired by customers, reflect and feedback into the next builds.
As seen from the Silicon Valley innovation principle just having a great idea is not enough; so it’s time for establish through the customer development process. Let’s see if the innovation and the information gathered about the initial idea is something customers actually want.
Usually it would be at this time people have discovered a great idea and then put all their funds to waste here after creating a excel document of hypothetical figures. The customer development process is a cycle of iterations which ‘Learns’, ‘creates’ and ‘Tests’ repeatedly until the successful business model is established. Every idea is built on assumptions and customer development turns these assumptions into facts. Collecting information is important to build effective innovation.
Overall, it is being prepared to fail and learn from this failure as not preparing to fail is preparation to fail.
12. Feedback Consolidation
After interviewing people you will be left with lots of information – Some useful and some not so useful. Use a grid to console all the validated hypothesis and invalidated and anything that may of taken you by surprise and strong emotion that was brought up by certain subjects.
To strongly validate a hypothesis you should be looking for customers that;
- Confirm that they definitely have a problem/pain point
- Believe that the problem can and should be resolved
- Have actively invested (effort time money learning) to solve this
- Don’t have circumstances beyond control that prevent from trying to fix problem or pain point (eg rules norms cultures stakeholders.)
13. Strategy Canvas
The strategy canvas is used to map out the benefits which are important to the customers.
13.1 Strategy Canvas
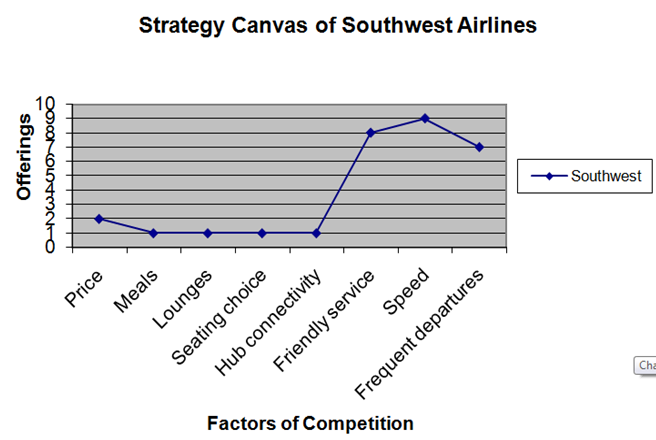
This information is a guide for innovation and could be used what direction branding would go in. It would also give competition leverage, in this case Short Haul Airline know what customers value in those airports. By implementing these factors and compensating for less important factors will attract those customers.
The least important factors are Meals, Lounges, Seating choice and hub connectivity. These factors could be scrapped and Short-Haul could invest money into the more important factors. This would include training staff for more friendly service, and more direct flights. Including more frequent departures could compensate on price as all the seats may not get filled. But, Short-Haul could use smaller planes, which the seats do get filled and use less fuel.
14. SWOT
This a tool to understand the big picture:
14.1 Strengths
- What advantages do you have
- What can you do better than other people/ organizations?
- What unique resources can you draw upon that other cant
- What do other people in the market see as your strengths
- What factors mean that you ‘get the scale’
- What is your organization you unique selling point
When looking at strengths compare them in relation to your competitors. If all your competitors provide high quality products then a high quality production is not a strength it’s a necessity.
14.2 Weakness
- What could you improve
- What should you avoid
- What are your competitors likely see as weaknesses
- What factors lose you sales
Internally and external to your business; do people seem to perceive weakness you don’t see. Are you competitors doing any better? Be realistic and face any unpleasant truths as soon as possible.
14.3 Opportunities
- New demand
- Market growth
- Economic upswing
- Social lifestyle changes
- New technology
- Changes in government policy
A useful approach when looking at opportunities is to look at your strengths and ask yourself whether or not these open any opportunities. Also look at your weaknesses and see whether you could open any opportunities by eliminating them.
14.3 Threats
- New market entrants
- Changes in customer tastes/needs
- New laws/regulations
- Threats from rivals
- Threats from substitute’s products
- Competitive price pressure
The outputs of the SWOT should not only help you understand the business better but should guide you on your next steps. Build strengths minimize weaknesses mitigate the threats and exploit opportunities.



![#3 Step Start-Up [Methodology] For Growth #3 Step Start-Up [Methodology] For Growth](https://allbusinesstoolkit.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/start-up-process.jpg)
![Causal & Effectual Thinking – Does It [Bring Results] For Entrepreneurs? Causal & Effectual Thinking – Does It [Bring Results] For Entrepreneurs?](https://allbusinesstoolkit.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Effectual-thinking.jpg)
