Some people love what others hate. Yes, there are certain times when people follow the bandwagen! But, everyone still has their individual taste.
What is the polarising effect? The polarising effect explains the different behaviours people have when they interact with your business. More so, it explains why some people love your products whilst, other people don’t particularly like them.
1. What is the Polarising Effect?
The polarising effect demonstrates the phenomenon that accrues when your brand is successfully positioned in a market. This phenomenon is useful because you are able to see why people are reacting the way they do when they interact with your business.
The Polarising Appeal Model (Created by Richard Wilde 2017)
So, we all know that in marketing if you find something that works, then you want to keep doing more of it. This model helps your evaluate those elements of your marketing activities as it explains everything has poles. The aim with this model is to actually discover the poles of your products so you can learn to embrace them or erase them.
2. Why is the Polarising Effect Important?
Russel Brunson speaks about this in his books Expert secrets. If you position your product well you will tailor it to a persons desires. You know that you have positioned it well because by making one group of people happy you naturally upset another group of people.
The people you upset will be on the other end of the pole. This is because of the mass marketing concept. By trying to please everyone you end up pleasing no one. You can’t possibly consider everyone opinion when trying to position your product. If you try and stay neutral with your marketing then you will fail and your customers will forget you (just like Nokia did).
It is almost as if you are ignoring the requirements of people and they feel left out. Russel explains how this is the best way of positioning themselves as because organisations that take the middle ground of the pole get forgotten. In other words, if a business that tries to appeal to everyone then it will not appeal to anyone (which is basic mass-marketing concept).
In turn, they fail. If people are reacting it means you are successful tapping into someone emotional state. As discussed in previous articles the emotional state is the direct link to a person subconscious. By which the subconscious is how we control a person’s actions, as subconscious thinking opposed to rational thinking makes 80% of purchases.
Nike is a great example of this…
When people buy Nike, they are not only paying for the quality of the shoes, but also the experience that is associated with athletically people. Pepsi also associates themselves with young vibrant spirit. These associations are very powerful when it comes to provoking a positive emotional response through the associated messages.
In turn, this idea creates conversational capital as well. This is the most powerful marketing because it is essentially word of mouth marketing. The more people debate and argue the more awareness your brand receives, and as the old saying goes ‘any publicity is good publicity’.
3. Background Information
Psychology professor Jordan Peterson outlines there are two types of thinking in human behaviour. These types of thinking are rational and emotional which massively affect our decision-making process. Zhang explains that people are divided into rational and emotional behaviour.
This further supports what Jordan is stating and outlines specifically how people are generally polarised. This is crucial when aiming to position your product messaging. When communicating with an audience there are two ways to do this, both rational and emotional. I will discuss this in more detail in the following sections.
4. Rational Appeal
The rational appeal is a method that attempts to communicate the products features, performance, quality and generally its usefulness.
Ken Orwig is a marketing strategist and he demonstrates that rational appeal is proof based on facts and statistics demonstrating logic the product performs as intended.
5. Emotional Appeal
By nature, human beings are less rational than they are cared to admit. We are in fact very emotional creatures.
Orwig asserts that people are far more engaged by empathy, fear, happiness, and sympathy. Marketers use many different techniques to appeal to these consumer emotions.
They take time to assess every detail carefully, including colour, tone, mood, and lighting (commercials).
6. Perceived Value
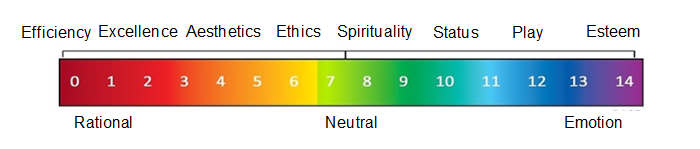
Interestingly enough, they are EIGHT ways to position your communication.
Copulsky highlights eight ways to appeal to a target audience message that stimulates the desired emotion.
Interesting enough these eight appeals of value can be split into rational and emotional ones.
Rational
- efficiency
- excellence
- aesthetics
- ethics
Emotional
- spirituality
- status
- play
- esteem
Rational and emotional can be seen as polar opposites.
When connecting these concepts together a new model is formed, and a new way of thinking as a marketer for an informed decision-making process.
7. How To Implement Polarisation
The theory is as you get older and wiser people to become more rational and base their decisions not on how it makes them feel but the facts behind that decision making. A marketer would use this information to position the message to be more factual if aiming towards an older audience.
However, a marketer can be creative. It is also known older people value events in their childhood. If you were able to tap into this information, then nostalgia could be a great emotional gain. When positioning your product and its message it is better to understand customer statistics such as age and demographics.
The premise is by targeting older people that share similar experiences, as a child will be emotionally attached to the product. However, those that did not would criticise it factually why it doesn’t fulfill its requirements.
Conclusion
I lay down a premise that the poles are segmented from rational and emotional given the distinction between brands such as Apple and Samsung. In addition, branding research demonstrates the power of emotional and an attachment to a business and its brand. In terms of positioning the messaging of a product – both the rational and emotional approach works well targeting the right audience. Generally, people are more emotional than rational as emotional is the links to the subconscious. Nevertheless, there are cases, such as B2B rational has the advantage over emotional (only in terms of messaging).
However, with no emotion or no rationality would hinder the messaging altogether. So, the conclusion is to play to your audience characteristics but be mindful of the positioning options you have available. When positioning to the emotional it has to be specific to the audience and those audiences that cannot relate to the advert or product only take the rational view. By this, they will be friction; even though for some reason it indicates them, it creates conversational capital that is always promotional activities.