Would the likes of WAP technology and millennium dome not of been such failures if they conducted better market research in the beginning?
Market Research definition – Market research is the process of looking to people in an industry that may be potential consumers in the future. The Research process includes asking questions and conducting interviews to understand everything the consumers want from your product that make it more desirable than the competition.
In this article, we will take a look at all the components that make an effective research plan.
1. What Is Market Research?
Market research is the process to gather data about markets and customers. This information is gathered through internal channels of a business as well as external means.
There are two reasons for conducting market research:
- The first reason is to improve existing products position to gain more understanding of the current products to improve your product positioning.
- The second is to Release a new product into the market. If you are looking to release a new product all together and you are checking seeing weather the market is viable.
However, before you can do either of these things you must do your research before hand. Otherwise you are taking a risk. Overall, you are able to gain some great marketing intelligence by evaluating internal data. This includes previous purchases, customer services data and information gained from people using your product in the past.
Although, in some cases, the internal marketing intelligence does not provide all the information needed for maximum insight and so you need to look beyond your business. Alternatively, external market researching is a systematic exercise to collect and analyse external to your organisation relevant to a specific market.
2. Why Is Market Research Important?
People’s wants and needs are changing all the time, often in ways that are subtle. With the purpose to innovate so then customers find new forms of value, so that having accurate and timely insights are massively important. Businesses have a huge appetite for information to go and for the most important part to make the correct decisions.
As a rule this will help organisations to understand the market potential, product satisfaction and the type of people in the market. Businesses can be in many different markets, in particular if they target many group of people within those markets. Then it is important to understand the general market the business operates.
Overall, informed strategies deliver increased competitiveness, remain sustainable on top of achieving growth.
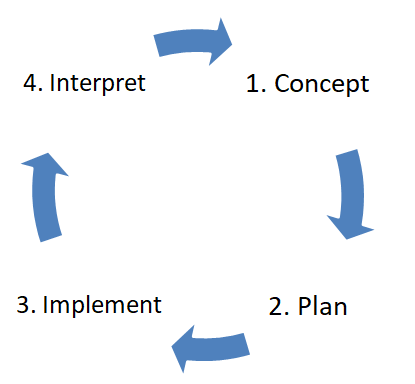
3. The Market Research Process?
The stand process for market research has four stages.
Four Stage Market Research Process
Concept > Plan > Implement > Interpret
4. Concept – Phase 1
Before, we can segment the market we need to outline a concept of the market.
This is broken down into two steps:
- Step 1 – defining the problem
- Step 2 – research objectives
This means we need to define our idea of the problem we are solving for our customers.
Once, we have outlined our idea of the problem, we can then outline the information we need, and the means of collecting that information in the research objectives.
Define A Problem In The Market
For both new and existing products, we need to define a clear picture of the problem.
Moreover, the products we offer solve the problem we define.
We need to conduct an investigation providing answers to the following questions;
- What is the problem?
- Who is the ideal customer?
- How this problem already being solved?
- Why our solution is the golden nugget (unique selling point)?
Remember: When trying to define the answers to these questions, it always useful to other peoples opinion.
5. Research Plan – Phase 2
This is also known as the research method.
Given the mass amount of information sources, we need to decide what type of information we require.
Assessing the Research Objectives
Because there are libraries of information, we need to understand what are objectives are and then access the information that meet our objectives.
Our objectives can be:
- The economic, demographic and life styles of people in that market
- Characteristics and behavioural patterns
- Retailer reactions, would they support it or stock it
- Forecast and potential market size
Assessing the Research Method
Once we have an idea that our objectives are we can begin to think where we get our information.
There are three forms of data collection:
- Internal market information – this is information your company currently holds. This can be within customer database, customer relationship management (CRM) system, customer services system or the website.
- External market intelligence – this is publicly available data sourced by publicly funded bodies, but most recent information capture potential market trends.
- Primary market research – if information is not yet available to meet your objectives then you need to go out and collect some for yourself. This means assess the most effective away to engage with the market and get the information you require.
To be able to answer the question, which is the right approach for my business? You need to assess what information you already get hold of and what information you can’t get hold of. The cheapest and fastest option is gathering your internal market information because this is free and you have it stored within your reach.
However, this will not always tell you the full potential of the market and it may be time to look outside the organisation. External market information can be beneficial, as it will save time and money in contrast to conducting primary research.
Collecting Internal Market information
Internally this can include looking at previous sales records, past purchases trends, existing product revenue, customer database and their attributes, logged tickets on your support site, customer services and complaints you have received.
Collecting External Market intelligence
This collecting data that is external to your business. External to the organisation we can also look at business data informational resources, Government data, and internet data.
Sources for Business data
| The Nielsen company (Nielsen.com) |
| Experian Consumer research (smrb.com) |
| Information resouces inc. (infores.com) |
| Arbitron (Arbitron.com) |
| J.D power and associates (jdpower.com) |
| Dun and Bradsheet (dnb.com) |
| Comscore (comscore.com) |
| Thomson Dialog (dialog.com) |
| LexisNexis (lexisnexis.com) |
| Factiva (factiva.com) |
| Hoover, Inc. (hoovers.com) |
| CNBC (europetv.cnbc.com) |
| Bbc news (bbc.co.uk/news) |
| Wordbank data (data.worldbank.org) |
Sources for Government data
| European Small Business Portal |
| European commission |
| International census |
| European Patient office |
| European Business directory |
| Euro pages |
Sources for Internet data
| Clickz |
| Interactive advertising bureau |
| Internet world statistics |
| Forrester |
Many of these sources sell information on demand and so to save time and precious resources you may want to outsource this information for a faster decision making process. You may find generic information using Google and other search engines but always make sure to look at the references to ensure is it a trust worthy source of intelligence.
Collecting Primary Market Research
You collect primary data when the is a gap of knowledge. By this, I mean data that you do not have access. Collecting primary data is by far the most complex, costly, timely and collected in a number of ways.
There are three types of research approaches;
- Surveys research
- Observational
- Experimental
Below I will speak about these in more detail.
Survey research
This is the method is used to collect descriptive information. Surveys tell you about people’s knowledge, attitudes, preferences and buying behaviour by asking them directly. Survey research is used to extract different types of information from different situations addressing just about all marketing questions they may have.
Advantages of using survey research
The advantages it is relatively fast and cheap to obtain information.
Disadvantages of using survey research
However, there is a disadvantage to this, which includes people not being able to answer the questions properly.
This is because surveys usually ask people questions of their previous experiences.
By which they are not able to interpret how they felt at that time, or not able to remember.
In addition, some people answer the interviewer questions so they appear knowledgeable (even though they do not know the answer), or may try to help the interviewer by giving pleasing answers.
Observational research
There are some types of information that cannot be extracted by asking questions. This is because there are some phenomena people live which they cannot explain. The only way to get around this problem is by observing how these people live their day-to-day lives. The philosophic approach used by academics to solve this problem is called ethnographic research.
This means to observe people in their naturally habitats to learn their behaviours. In addition, marketers are also observing what people are saying. The process of doing this online is called webology. This is via the internet, by following your target audience conversations on blogs and social networks. This is useful as it obtains naturally accruing feedback that cannot be gained through means that are more formal.
The benefits of using observational research
The benefit of using observational research is learning about people desired. As you understand their day-to-day lives you know, what it is they want. Henry ford famously quotes: if I had asked people what they wanted they would of said faster horses. By gaining the feedback from the target audience the dream of the automotive would never of come to life.
There negatives of using observational research
There are also some negatives when it comes to observational research there are some things that cannot be observed. We do not understand peoples feeling, emotions, attitudes, motives and private behaviours.
Experimental Research
There are two approaches for experimental research.
- Causal
- Effectual
Effectual means of assessing
- Exploratory data – Capturing preliminary data to deeper identify the problem and suggest a hypothesis.
- Descriptive data – descriptive research is to identify market potential, demographics and customer behaviours in that market.
Effectual is a new form of research that is conducted online daily through content marketing. This includes observing the feedback through the analytics to monitors blog posts and other content posted online. This could bring valuable insight in what topics to post about in the future.
The experimental elements is after observing the data forming a blog post to match the data and observe how to audience reacts. This could also lead on to valuable insights for product and other opportunities within the industry.
Casual means of assessing
- Competitor data – this is discovering all the different ways this problem is being solved in the market already.
- Authenticity data – this includes testing each hypothesis and analysis the causes and effects of each approach.
Causal include Experiments include selecting matching groups and giving them similar treatments, controlling unrelated factors and seeing how people react. Thus trying to explain cause and affect relationships.
This monitors two different prices for the same product, or the variation of products in a specific location.
6. Implement – Phase 3
This is deciding where, when and who are the people you want to collect information from and the best way to collect this information.
Internal Market Research
If you do not have an automated system, the information will need to be optimised.
You may have information located in different areas of the company. This will need to be collected together into one system ready for analysis.
External Market Intelligence
This will just include going out and gathering the information from the required sources ready for analysis.
Primary Research – Deciding Your Contact Methods
After deciding your research method you will go out to the respondents and interacting with them, collecting the information ensuring everything is being followed corrected in the planning stage. After you have decided your research method, you now need to understand your contact channel.
Research contact methods are those touch point between the researchers and the respondent. To the question you should be asking at this point is: Who do we want to speak with? And, how do we access these people?
The four main contact methods are mail, telephone, personal and online. Each one of these methods has both their strengths and weaknesses.
The form of data collect from mail is questionnaires. Mail may provide some problems as some respondents may not understand the question and they is not a researcher at hand to explain. There has to be some incentive otherwise people will not respond or the respond rate can be quite timely.
When taking into account the costs of printing and offering incentive to get a strong data set can be quite costly. In addition, it is important to be aware of external influence that may skew the data.
Telephone
Telephone offers more benefits than mail as you get instant feedback and able to explain the questions. However, there are problems with bias so the researcher has to frame questions in natural way. The costs can be high as it is required that you buy a data set of phone numbers from information provider.
Personal
A method for personal is using interview. There are two types of interviews: individual and group interview. These both include speaking to people face-to-face in a controlled environment.
Overall, there is a lot more flexibility when it comes to personal contact and if you want to understand personal behaviour this is on the most part is the only effective approach to take. However, it can be massively expensive, timely, have ethical implications and required heavy planning. Nevertheless, the data received is very rich data, which will provide a massive insight.
Online
This includes internet surveys, online panels, experiments, online focus groups. By the efforts of being online, we can experiment with prices. The results collected are much faster and you can collect a lot of information just using the statistics.
Such as, Google analytics and other online tools for very low cost and automate big amounts of data. However, by using the internet marketers are able to take their researching effort further than ever before. Researchers are listening in on people conversations through blogs and social media they are able to mine the rich veins of unsolicited, unstructured bottom up conversation flows with detailed context.
6. Interpret (Data Analysis) – Phase 4
There are two forms of data analysis. The first is a basic analysis, which is at descriptive level. By this, I mean it is frequency tables, stand deviations, or comparative basis such as, t-tests and cross-tabulations. The more advanced analysis is looking for relationships, group respondents or cause and effect.
- Relationships interpretation – regression analysis
- Group respondents – cluster analysis
- Cause and effect – analysis of variance techniques
You must interpret market research results with great care. A common failing is to conclude cause and effect from a hunch. For example, we see a pattern that sales rise when advertising levels increase. However, this may not mean increasing advertising expenditure will lead to increased sales.
This is because other marketing variable need to be taken into account. For example, it could be that sales force interaction may have increased at the same time also.
Conclusion
When conducting market research be sure to follow each stage in a linear way.
It is also important to ensure to be very clear what your objectives are and how these objectives will contribute to the ROI in your business.
Have a clear plan to achieve these objectives and the types of information you need to support your findings.




![#10 Strategic Positioning Tools [Used By Corporations] Proven To Work #10 Strategic Positioning Tools [Used By Corporations] Proven To Work](https://allbusinesstoolkit.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/What-is-Strategic-Direction.png)
![#50 Top Factors [Link Building & Penalties] For Off-Page SEO #50 Top Factors [Link Building & Penalties] For Off-Page SEO](https://allbusinesstoolkit.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Off-Page-SEO-1.png)