The ability to focus all your energy on the right tasks will be detrimental towards your success rate. But, how do you know which tasks to focus on, especially in this realm of SEO when there are tons of controversial views that cloud our vision.
What are the four pillars of SEO? Search engine optimisation is the process of using best practices to have your website appear on Google search engine. It is made up of FOUR building blocks that are essential for your ranking success. This includes: website as a business, site-level optimization, page-level optimisation and off-page optimisation.
In this article, we go through the top-level considerations when first coming to build your SEO. So I have broken the SEO process down into four pillars.
1. What Is Search Engine Optimisation?
SEO is the process of optimising a web page in such a way to increase the likely hood of a Search Engine Result Page (SERP) ranking Position. It is explained by many professionals that there are FOUR pillars for driving traffic to your website.
Below image outlines the four pills of SEO
- Website as a business – generally more niche websites are more successful in search result as they are more relevant to searches
- Site-level Optimisation – this can includes things such as site structure and loading speed.
- On-page optimisation – this can include those elements that are integrated into the web page and indicts how the website functions. This includes; design, the location of elements, content, alt text, funnels and direct conversions.
- Off-page optimisation – this can described those activities that are external to the website (this includes back-links, social media and paid advertising).
Google’s whole business model is to protect the relevancy of their search engine results page (SERP). This is because they want to deliver the best result to their users to remain ahead of the competition in the industry. Google have built a set of guidelines of do’s and don’ts that SEO specialists should follow at all times if you want to be rewarded by the top SERP. These guideline all persist around a single factor of providing the best experience to the visitors as possible. We call this user experience (UX). This means the web pages that provide higher user experience, better serve that visitor and win the higher spots in the ranking. As a result, have a greater number of visitors that click to your website.
2. Why Is SEO Important?
In the simplest terms, strong SEO improves your internet visibility. This means that the more people who visit your website, the higher your online traffic will be, and the more likely you will be able to sell your product or service to a larger audience. There are businesses that make a living off where they rank Google search results.
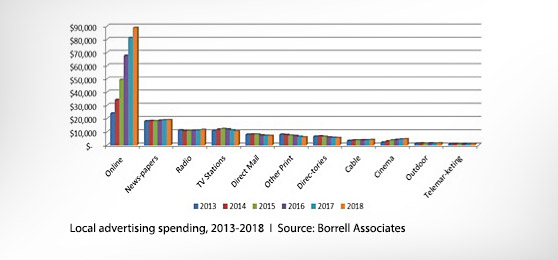
Online advertising spend
The internet has become an extremely crowded place and everyone is trying to hit the higher spots in the search engine results page. The lower a website’s ranking, the less likely it is to be visited by a potential consumer. As a result, achieving a high Google position is critical. Even if consumers don’t click through to your page right away, they’ll see it in the search results, which will improve your brand awareness and familiarity.
3. Website As A Business (Niche Level)
There is only one reason to build a website….
…and that is to make money.
As we all know a business is the means to make money where ever you are in the world. In that case we can agree that our website is a business, and so we should treat it as such. SEO marketers define this pillar as finding your niche, which basically means who is your customer, what is the market and how do you bridge between them.
User Experience
Because the internet is becoming over populated means there is a big chance that your will experience competition, especially for those high volume keywords. This means in order to beat the competition we need to deliver a better user experience than the competition. This includes value, and relevancy to get the traffic to our website and monetise it, to support our bigger business objectives.
In addition, a site that blatantly breaks these rules can still gain ranking but at a risk to be blacklisted by google and other search engines. This entails the web page to be dropped out of the index and not found in the search results. These businesses have no option other than delivering the best UX because Google doesn’t want insufficient websites in their search that provide little relevance to their users.
Strategic Position
Just like any aspect of business, this means we need to be strategic.
- Establish your heading
- Outline your direction
- Target customer
- Products
- Funnels that fit into the wider business environment
- keywords and volume of traffic aimed to support the business objectives
- Wire frame of your website
Just like any aspect of business, a strategy is well informed with real life data. This also means that the keywords we wish to rank for are achievable but also bring relevant traffic to our website. By relevant traffic, I mean traffic that have a desired action or interest related directly to your content and product. Otherwise, this will result with a low user experience, which will be demonstrated by Bounce rate.
4. Site Level SEO
Now we have a clear plan with all tasks, keywords and wire-frames broken down we can begin to build the website. This leads us to our second pillar which is the site level optimisation. This includes building and optimising those global areas of the website and the server.
The typical tasks include optimising:
- Site layout and architecture (site maps / bread crumbs) – Your website needs to be as easy to roam as possible. This required a good plan to establish a hierarchy of the website against its purpose.
- Loading speed – Even though this can differ page to page, your website has to load less than 3 seconds.
- Mobile Responsiveness – There are more users online using mobile than desktop nowadays so having it mobile responsive serves your users best interests on mobile (header section of your website, footer section of your website and side bar of your website).
- Server Delivery – Ensuring the server bandwidth is acceptable for predicted traffic, whilst also delivering the website data over the internet as seamless as possible.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) – If you have a global business that is heavy with features you need to lose less value features or install a CDN.
- Caching – Caching is storing data on a visitors device so it has to load less the next time a person visits.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) – Ensuring the website is secure with an up to date SSL.
- Root Domain Factors – This is having a domain that is relevant to your niche but also least amount of characters as possible.
- .HTACCESS – This includes any redirects you wish to address and forcing your website to always direct to HTTPS for security purposes.
- Duplicated Content – Duplicate content throughout the website suggests to google your website may not deliver a good user experience.
- Legal – If you sell products or collect information then you want to ensure you have a terms and conditions page to abide the GDPR laws.
5. Page Level SEO
Now we have built and optimised our website we can begin to build content.
This takes us to the third pillar of SEO on-page optimisation.
Page Level SEO tasks include:
- Keyword SEO – This is ensuring the web page has the keyword seen in relevant places.
- Content – This is building content that is relevant to the keyword in question. This keyword has to meet the requirements based on the competition. In general, I would suggest to build a new website anywhere from 20 – 50 relevant blog posts depending on how competitive the niche is.
- Call to actions – This is ensuring the users take the action to meet the business requirements of having the website in the first place.
- Page Loading -There may be elements on a single page that prevent the web page to load within the desired loading time and so this needs to be addressed.
- Tagging and mark-up – This includes using the correct headings and schema so Google can understand more clearly what the web page is about.
- Mobile – Again, there may individual elements on a page that are not mobile responsive.
- Links – Having links in the content going to other areas of the website and other websites is a factor Google takes seriously.
- URL – This is ensuring the link extension is static and easy for the user to interpret.
- Page Structure – When a user first enters a web page they will have a question in their mind. This is usually the whole reason they are there. Addressing this question early on is important. Furthermore, when they get an answer to this question they will then have new questions, which all need to be established and addressed.
- Brand Signals -Building a brand is always important; Google also recognises this as well.
- On-page Risk, Issues & Web Spam Factors – When building page content we always need to be mindful we do not break the Google rules.
- About Us Page – For Google to trust your website they are starting to take more care in your about us page. You now need to prove your worth in the industry, which is basically a CV in the about us section.
The on-page SEO main priority is trying to create web pages that are engaging to the audience and have the right call to actions to meet our business objectives.
6. Off Page Level SEO
Now we have created the basic website and it ready to ship, we need to get people to see it. The fourth pillar is optimising channels off the website.
- Paid advertising – this deliver traffic to your website using tools that your pay for such as PPC, Facebook ads or generic website ads.
- Google my-business – this will tell Google who you are and more about your intentions for them to understand your priorities better.
- Position Zero – the are certain activities you can do to increase your chances of being on position zero which will be more effective than position 1.
- Back-links – this is having high domain authority from websites pointing towards your website, and disallowing those sites that may harm your authority.
- Social media – I use social media to generate a massive amount of leads to your website.
- Email marketing – as part of the on-page objectives there will be a call to action to build contact details, mainly email for marketing purposes later on.
- Off-page risk, issues and web spam Factors – ensuring you abide the web spam factors.
This is mainly down to channels of promotion and generating some good domain authority juice from back links of external websites pointing to your website.
Conclusion
The truth is SEO is not that hard to do! and anyone can do it… You don’t need to have Albert Einsteins brain in order to do well. In fact, this topic is surrounded by confusion because there are so many controversial views.
The #No1 key factor for success is thinking orderly and structurally. This is because you can save hours of time and effort if you just know everything in the SEO world fits together. When building an SEO strategy it is always easier to know what areas of the website you need to optimise.
When conducting any of these activities you must have a results driven focus. For an off-page strategy you will focus on the channels that bring the most traffic, link building and click through rate. Whilst an on-page strategy you will focus on keyword volume, bounce rates and content.