After, exhibiting a marketing conference just recently in particularly the topic of ethical marketing was discussed. The most important learning from this experience was how this term has not yet made its self into the realm of academia. On the contrary I have wrote this post to outline the points and a detailed summary.
This is a term that has not yet made itself into academic literature. Ethical marketing is the practice to ensure all business activities are conducted in a moral manner.
In this article, we will go through the origin of this terminology and outline why we should be discussing it in our modern marketing practices.
1. What is Ethical Marketing?
Ethical marketing is as simple as always telling the truth and communicating to your stakeholder honestly and with integrity. It is having the responsibility too always promote honestly in all your marketing campaigns, advertisements and personal relations.
In general, one of the main purposes for marketing is to communicate your business to customers. However, when we communicate the truth, may not always deliver a favourable opinion by stakeholders.
This paradox is why people behave unethically. To that end, we must always ensure we approach our business activities being mindful of social responsibility we hold.
These means not lying about the intended message and avoid exploiting vulnerable people when leveraging your mediums and channels.
2. Why Is Ethical Marketing Important?
Ethical marketing is important for two reasons:
- Customer Perception (the way people think about your business)
- Increase Productivity (sense of fulfilment makes you work harder with more motivation)
Together, this will improves the overall performance of your business. We will discuss these in more detail below…
2.1 Customer Perception
Until recently, even tobacco firms have been promoting their products as being not addictive. Some firms also place their advertisements in locations that exploit vulnerable people.
Many studies show that dieting and diet pills are ineffective. However, with clever marketing tactics, firms use exaggerated messaging that taps into a person’s life. To that end, firms have been guilty of promising lies in exchange for money.
We now live in a very connected world. Whereby, we recognise these tactics from a while away. Furthermore, because of the internet we can share our experiences in a matter of seconds. Thus, exposing these firms as fraudsters whereby there business will fade with them.
More interestingly, we can see this everywhere today as it makes business more competitive in terms of revenue and productivity. In 1992, Coop Bank conducted a report to find why customers shop there.
The results showed it was because they had no direct relationship with apartheid South-Africa. Coop later went to embody this image and refused dealings that were unethical (Leigh, 2013. P. 28). People were choosing Coop over its competitors because of their ethical behaviour.
At first, Coop did not embrace its ethical dealings, but they found people were shopping there for that reason. They later embodied this as part of their marketing campaign and it massively boosts revenue.
2.2 Increases Productivity
Ethical marketing also increased productivity in the workplace.
Tom Monahan, CEO of the Corporate Executive Board states; “What we found is a strong link between ethical cultures and employee engagement. If an employee works for a company they consider having a strong ethical culture they work harder, stay longer, and are less likely to leave. Collectively, this data points to a 9% productivity boost from ethical leadership in the management ranks.”
The reason we risk our lives to save someone else’s life is that it makes us feel good.
This is because we like to feel that we are part of the solution in the world.
For example, we feel good to give our money away to a charity for nothing tangible in return. Therefore, the incentives for purchasing from an ethical corporation are even greater.
Overall, this helps us build a strong brand image through the means of brand association. Moreover, this is a form of connecting to people through emotions.
3. The Ethical Marketing Landscape
Ethical marketing is central to the operation of a business.
3.1 The ethical marketing landscape
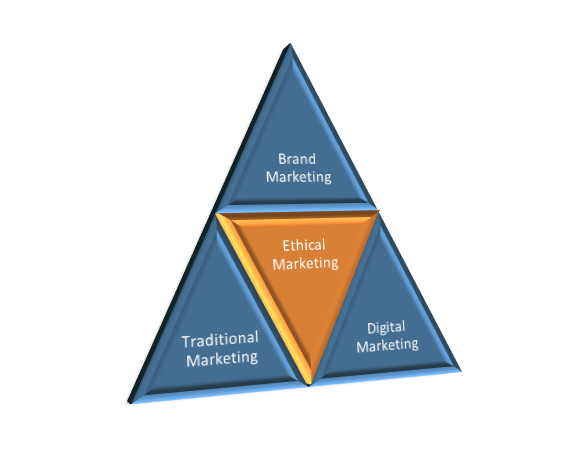
As you can see from the above image every action you take as leader will influence the surrounding areas. These are areas are brand marketing, traditional marketing and digital marketing.
4. Real Life Examples of Ethical Marketing
Way back when I was working for a world leading engineering firm I was always told to follow the corporate social responsibility protocols. In fact, we had a set of rules to follow that were made by the firm.
Under vigorous market research, and attending trade shows every aspect of the market was calling out for cleaner vehicles. This was one of the reasons we positioned our whole business towards electric vehicles (EV’s).
At this time, EV’s were not even our biggest customers. Nevertheless, the data showed us the demand for cleaner vehicles.
Everyone wants to save the planet
Yes, it is true we are saviours at heart and more recently, we can see more corporations following this trend. Furthermore, we see the Green energy and people striving to reduce their carbon footprint all over the world.
4.1 Adidas
Adidas have been able to innovate plastic waste into the material of their trainers.
4.2 Asia
Another example, include the practices in Asia. They are able to eliminate the need for GEO-engineered food and pesticides for the production of vegetation. They are using ducks to eat the weeds and clear the fields of bugs and other nasty insects that ruin the production. As a result, reduce the risk of cancer and other fatal diseases caused because of these unethical food production methods.
5. Real Life Examples of Unethical Marketing
5.1 Lehman Brothers
For example, Lehman Brothers CEO Richard Fuld is a good example of this. A week before Lehman Brothers bank folded Richard Fuld assured stakeholders that business-as-usual, even though they were losing billions every day.
5.2 Apple and Samsung
In more events that are recent, Apple and Samsung have been exposed of slowing down their older phones, whereby they have been fined a total of 15 million euros (DigitalTrends, 2018).
They have been suspected of doing this for years now, but they always told their stakeholders this was not the case.
In the above example, the communication from business to stakeholder was unethical which has resulted in disastrous effects for business in both share value and public opinion.
5.3 Volkswagen
On the opposite side, the Volkswagen emissions scandal absolutely destroyed their profits in the US and Europe.
The Volkswagen emissions scandal was an attempt to avoid the higher development costs because of tighter regulations set by the government. This involved Volkswagen CEO to approve and create a system for cars that allowed them to falsify the result of the emissions let out into the atmosphere.
As a result, their cars were releasing a gas higher than what was legally required.
Not to mention that they had to recall 11 million vehicles altogether, but this scandal resulted in people no longer wanting to buy this brand of cars for their future sales.
6. Markets and Sustainability
As evident from the previous section, looking at social trends is a clear indicator of how we should approach our marketing activities and the definition that surrounds them. Schumpeter (1942) provided a very interesting theory that has more relevance in modern times.
His theory, Creative Destruction sets a clear base of today’s modern definition. I would like to discuss the Waves of innovation, which is an adaptation of Schumpeter’s model (please see below).
6.1 Waves of innovation (K Hargroves & MH Smith, 2005)
Since the industrial revolution, the development of society comes in different forms of innovation.
As you can see from the above image, we are in the 6th wave of innovation. This wave is being sustainability in an ethical sense. The idea, of this concept, is that if a business does not adapt to the current wave they will not survive.
This is evident in businesses such as HMV.
7. #7 Principles of Ethical Marketing
7.1 A Common Standard of Truth
The first principle is to ensure that you are as truthful as possible when you communicate to the outside world. This also includes avoiding bias and prejudice.
It is important to point out that people can spot this behaviour from a mile off and it can only result in people losing trust in your business.
7.2 Being Transparent in Endorsements
The second principle is to ensure that people are aware of your business intentions. A lot of corporate businesses fund societal programs, and politicians in hopes this will bring them control in competing markets.
Moreover, by trying to hide your endorsements is a sign of a business is committing forgery or trying to bribe to popular opinion.
7.3 Operational Standards
The third principle is ensuring your business process runs smoothly providing that the day-to-day tasks do not harm anyone or anything.
In this situation, it is important to report to senior management and highlight the ethical operational issues.
In addition, keeping a moral working environment will increase the satisfaction workers have.
7.4 Exploitation of Vulnerable Consumers
The fourth principle is making sure you are aware of any vulnerability your customers may have.
If these vulnerabilities are addictions then you must try to have standards. For example, the betting community have a spending limit in their casinos.
7.5 Data Protection
The fifth principle is to ensure your consumer privacy and personal details are safe in your hands.
With the intention to keep them in a safe place away from hackers and not selling information to third parties will build an element of trust with your customers.
7.6 Comply with Government Regulations
The sixth principle is again an element of trust. Whereby, it is important to abide the standards and legislations set by the government.
This is also being that people who break the law cannot be trust worthy.
7.7 Ethical Implication are Openly Discussed
The seventh principle is discussing the impact your actions may have, and the repercussions are openly and honestly assessed within making business decisions making process.
8. Unethical Marketing Practices
8.1 Surrogate Advertising
Surrogate advertising is promoting illegal products in disguise of another product. There are laws that do not permit certain advertisements such as cigarettes and alcohol. The surrogate advertisement would be promoting electric-cigarettes in place of the traditional smoking method.
8.2 Exaggeration Promotion
Exaggeration promotion is overemphasising the capability or message of your product and service. Because even though there may be some truth to an overemphasised message there is also some lack of truth. Exaggeration advertisement can be seen in popularity, features and capabilities.
8.3 Puffery In Advertisement
Puffery advertisement is focusing on the subjective claim that cannot either be proven or disproven. Rather than objective claims, they are disguising the true nature of their product.
8.4 Unverified Advertising
Unverified advertising is promising results without evidence.
8.5 False Brand Comparisons
False brand comparisons are making misleading claims about how brands products compare.
8.6 Exploitation In Advertising
Exploitation in advertising is taking advantage of vulnerable people being addicts or children. Both addicts and children consume huge amounts of advertising without being able to evaluate it objectively.
Conclusion
The roots of ethical marketing goes deeper into the business operations. Marketers, especially PR and Advertisers must know what goes on in the business operations and the results of using their products and services.
The responsibility is on the marketers because false promotion, and ignoring the truth is a breach of ethical behaviour. Even ignoring the matter and not communicating about this to stakeholders is still considered unethical.
Overall, it becomes evident ethical marketing can affect us in many ways. From the products we sell, who we deal with, what technology we use, to the way we conduct business.
The idea of marketing is less about forcing your product on someone that does need it or want it. Rather, delivering something to customers they actually want and need to solve a problem in their life. This result in taking a more value-driven approach is a long-term solution.
More precisely, using data to find where your target customers are, what needs they have and create something they actually want and deliver it in an ethical manner. This will lead to greater customer satisfaction, which leads to the most powerful marketing approach (Word-of-mouth).
References:
- DigitalTrends (2018). [online] Digitaltrends.com. Available at: https://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/apple-and-samsung-fined-italian-government/ [Accessed 28 Oct. 2018].Leigh, A. (2013) Ethical Leadership: Creating and sustaining an ethical business culture. London: Kogan Page.
- Monahan, T. (2009) ‘The Role of Business Ethics in Employee Engagement’,.
- Schumpeter, J. (1942). Creative destruction. Capitalism, socialism and democracy, 825, 82-85.
- Solomon, M., Marshall, G. and Stuart, E. (2013). Marketing: Real people, real decisions. Pearson Education.
- Zerolimitweb (2018). Organic SEO vs PPC in 2018: CTR Results & Best Practices. [online] Zero Limit Web: SEO Expert in Los Angeles. Available at: http://www.zerolimitweb.com/organic-vs-ppc-2018-ctr-results-best-practices/ [Accessed 9 Sep. 2018].
- K Hargroves, MH Smith (2005). The Natural Advantage of Nations: business opportunities, innovation, and governance in the 21st century






Your website has excellent web content. I bookmarked the site
Woo! thanks 🙂 if you have any questions, or anything you want help with then be sure to let me know and I will try my best to help!