Market positioning is extremely essential to your business strategy as it gives a clear indication what your customers perceive is being offered to them.
Market Positioning is the process in marketing of establishing your place in your market. It is devising a direction that matches your target customer preferences. Mainly, your market position justifies the promise you are delivering to your customers.
In this article, we are going to dig into the four areas of your business you need to position.
1. What Is Market Positioning?
Kotler, one of the most notorious marketers in the academic world and he describes in his book Principles of Marketing that market positioning is the way a brand or product is defined in the consumer’s eyes.. In this very book, he tells us that positioning is the place a product occupies in the consumers mind against competing product.
This is because whilst we build our products in factories, we build our brands in the minds of people.
Therefore, there are many main aspects to consider when looking to position your whole business. From my experience I have identified FOUR main aspects that you need to consider:
- Strategic Positioning – strategic positioning is the overall direction of your organisation. This is answering questions like, what is your vision, mission and goals?
- Brand Positioning – the brand position reflects everything you are as a business, which is carefully examined to ensure this brand image actually delivers the intended message to the customers.
- Product Positioning – the position of the product examines what problem does it aim to solve, that is a cause of pain in the eyes of the consumer.
- Customer Journey Position – this outlines what message we display to the customer to increase the speed of their purchase. The idea is to break down barriers that may prevent a person from purchasing by giving specific answers to the questions they might have.
Overall, these FOUR aspects of positioning outline 2 very important questions (this includes):
Question 1: Which customers do you aim to serve?
- Market Research (Learning more about the market and all the types of customers in that market)
- Market segmentation (assessing the groups of people in the market)
- Targeting (evaluating which market segments to focus on)
Question 2: How do you aim to serve them?
- Product differentiation (what value are we delivering that the competition is not?)
- Market positioning (how customers perceive the brand and the usefulness of the products?)
2. Why Is Market Positioning Important?
In many cases two or more firms may compete for the same position in the market. During this instance each company will have to find creative ways that set themselves apart.
They must differentiate what they offer by building a unique bundle of benefits that appeal to what is valued within the substantial group and segment.
A brands positioning serve the direct needs of well-defined target groups of people and more importantly communicate that value effectively above the all noise of competing business.
3. Positioning To Cut Through The Noise In A Market
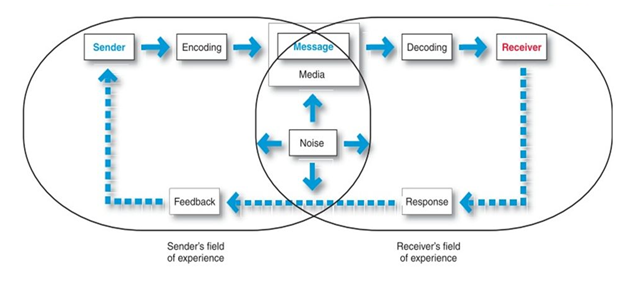
When we refer to noise, we are talking about all the advertising that is happening in an industry. Each advertisement is targeted to a specific person. However, it is usually heard by many types of people. This is why refer to it as noise, because the message may not be targeted specifically to your customer.
The closer the position matches to the demands of the customer, the higher chance of cutting through the noise. So the idea is that your want a message that is not noise and resonates in the minds of your target customer.
Part of doing this you need to understand your market position. But, more so understand how communication is encoded and decoded in the minds of the consumer.
3.1 Communication Model
McDonalds and Starbucks coffee products are perfect examples of successful positioning.
Even though they are direct competitors (selling coffee) they have differentiated and positioned themselves to serve different markets. They both offer different product assortments and in store atmosphere – yet each is extremely successful.
This is because they are not directly competing against each other.
4. Marketing Positioning Process
Prior to positioning, we have done the following:
- Collected all the market research data
- Segmented the market data
- Estimated good targets
- Created detailed profiles of these target segments
- Create a positioning strategy
- Execute the positioning strategy
- Review and control
- Re-position
Overall, a really effective positioning process will go through these 8 steps very carefully.
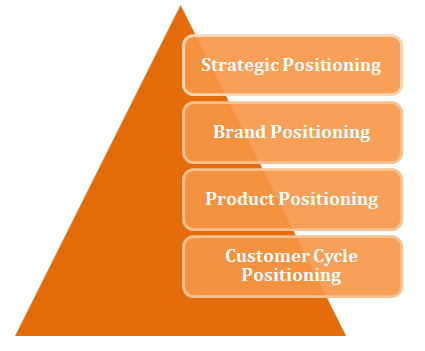
5. The Four Pillars Of Positioning In A Market
There are FOUR pillars of positioning in marketing.
The FOUR pillars are broken down into strategic positioning, brand positioning, product positioning and customer cycle positioning.
They are successful because they create just the right value proposition for its mix of customers (Armstrong et al, 2014). The positioning consists of three steps:
- Identify a differentiating set of competitive advantages
- Choosing the right competitive advantages
- Selecting the positing strategy for each pillar
When we go about the process of positioning, we should follow this process linear starting with the strategic position.
5.1 The FOUR Pillars Of Positioning
I have separated the ways of positioning into four pillars as these commonly confuse people.
6. Strategic Positioning
Strategic positioning is Identify a set of advantages that can make you more competitive in the market.
These advantages are different from what people in the market are already targeting.
To build profitable relationships with target customers, marketers need to understand and can deliver and differentiate its products to provide superior value to its customers.
If you are able to do this better than the competition then there is potential option for you.
This is because we do not build a solid position on empty promises.
Companies must do much more than just shout about their products. They need to deliver the intended promise of quality and performance.
Ways you can differentiate?
To find points of differentiation a marketer must think about the customers experience with the organisation, product or service.
Companies with excellent marketing departments will find points of differentiation at every touch point.
When conducting a positioning strategy, you need to assess the following:
- Product differentiation – includes competing on features, performance, style, and design.
- Service differentiation – includes competing on support, maintenance and delivery.
- Channel differentiation – this includes how customer get access to your product and service. This is usually the key factor key convenience and businesses can set their self apart from the ways they design their channels coverage, expertise and performance.
- People differentiation – this includes hiring and training people better than the competitors do.
- Image differentiation – a company should portray a products or services with distinctive benefits that appeal to the target audience better than the competition.
7. Brand Positioning
The positioning of the corporate brand is the overarching image of the company.
This is following the guideline from the strategic position.
It is identifying the type of message, which is important to the main target group of people.
For example, what do people think when their customers hear apple.
Apple have spent years to build reputation and building this reputation into associating colours/imagery.
8. Product Positioning
Product positioning is how you place your product in the market against the competition.
Apple have cleverly analysed where the iPhone best fits in the premium phone market.
They use attributes such as pricing and the user interface of the phone to establish this position of a premium product.
The basic colour and imagery branding of this product correlate to the overarching brand image.
This is because when positioning the product it has to follow the rules of the corporate brand.
However, when we communicate our product we want to focus less about the aspects that make our product different, but focus on the results the user can get using these differences.
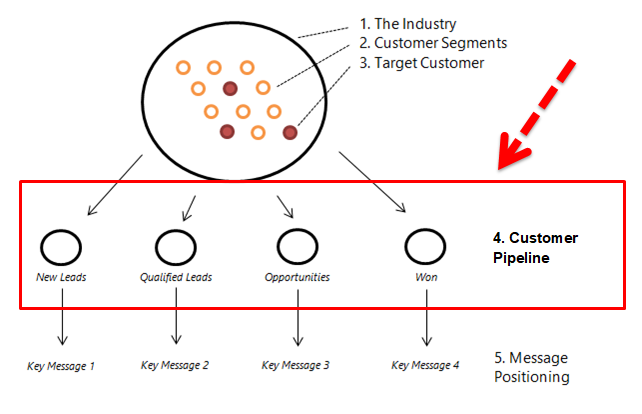
9. Customer Cycle Positioning
The positioning of the customers journey is finding out what type of message is important to that customer against what stage they are at in their purchasing process.
The customer journey is a term used to try and understand the road map customers take to learn about your brand and make a purchase. There are different phases a customer has to go through before making a purchase and it is marketing role to understand which phase our customers are at.
These phases are called the pipeline and we leverage this by having a message to correlate which phase they are at in the pipeline. This means that the message will address both the target segment and the phase of the pipeline.
The customer cycle position is outlining where about the target segment is located in your purchasing funnel.
Are they new leads, or have they already made a purchase before?
9.1 Customer Pipeline
New leads are those customers that have got first contact. This being the first time on your website or the first time they have step foot in your shop.
Qualified leads are those people that have shown interest in your product by interacting with the website or any marketing event.
Opportunities are those people who have reached out to the organisation either asking questions to understand how we can solve their problems.
Won is after they make a purchase and outline re-targeting and customer relationship building activities.
This is important because people that have just been introduced to your business they are going to have gaps in their knowledge about your business. People will most likely be asking:
Who are you? (You may respond with a brief of your company)
Why can I trust you? (You may respond with testimonials)
Whereby, if someone that has made a purchase may be asking questions like:
What other value can you offer me?
It is commonly known that brands such as apple tailor the messages they send out via social media to suite the target audiences of those channels.
Conclusion
The markets much know the lay of the land when creating marketing messaging.
So, then know exactly the position they want to put. By blindly throwing out some marketing collateral may been competing again a better-suited competitor or reaching no one at all.





![#10 Strategic Positioning Tools [Used By Corporations] Proven To Work #10 Strategic Positioning Tools [Used By Corporations] Proven To Work](https://allbusinesstoolkit.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/What-is-Strategic-Direction.png)