Everyday working as a digital marketing executive I used to sit at my little desk and constantly ponder the same question…
…is my strategy working?
The reason for this was because whilst studying none of the literature put much emphasis on the importance of tracking. It seems obvious to me now to track everything.
Marketing is the bridge that links people to business. It is creating NEWS WAYS to make and maintain sales by steering people mentally and emotionally towards a purchase. Whilst tracking interaction between you and your customer.
1. What Is Marketing?
Marketing is creating new ways to make and maintain sales over the year.
To do this a business must be creative and have better innovate solutions for the people in the market in the market place. Every marketer should be looking forward to stay ahead of the game.
However, the only way we know our efforts are working is by tracking everything. You try a new strategy you want to track it.
So the strategy will usually be about informing customers, employers and lenders of the benefits our product and services can offer them. These benefits can come in all different ranges of products and services which meet a demand in the market.
However, before you can do that you need to understand who your target audience is. This means implementing a system that gathers market info is crucial. This is because once you realise the type of people in the market, you can begin to tell these people about the amazing products and services you can offer them.
Josiah Wedgewood (1730-95) became known for their ability to sense what a market wanted in terms of design, quality, and price.
They leveraged this information by organising production to meet meet these demands.
More so, there business model of transforming raw materials to the final product was saturated by the customers intended value.
Value is captured by outlining a customers wants and needs.
By forming a list of wants and needs you can understand a problem in someone’s life.
Being able to communicate these wants and needs is the primary goal to a persuasive message.
1.1 Do Not Be A Laggard!
A common approach people take when building marketing strategy is copying the competition. Business are moving rapidly now across all industries, which means they are creating new forms of value. Any business should be looking to pave the way, and not playing industry catch up.
By copying the competition this is essentially what you are doing.
…how can I possibly be offering new ways to make sales by copying to competition?
Yes this seems like the safe approach, but this means the only competitive advantage you can deliver is by offering your products cheaper. Which is the fastest way to kill a business growth in the long term.
Overtime, I have come to realise that there are three types of businesses.
- The first are those that know what are happening
- The second are those that are waiting for things to happened
- The third are those that think… Wait… what just happened
This is something I like to refer to as being a laggard, which is risky for any business.
1.2 Marketing Example
If you have been strolling through town on a Saturday night and seen people on the street handing out flyers promoting a nearby club.
These people are marketing.
All in all the aim for these people is to persuade you to enter the club they are promoting.
They will plan whom they hand flyers to, where they stand, and how they approach you.
In addition, the flyers will include some sort of promotional discount, like a free shot as an incentive to visit.
If they have done their research right, they would have persuaded you to that club.
This often works by demonstrating the benefits of going to the club, and if the incentive is greater than the inconvenience then they are offering value.
If this is the case you may find yourself entering the club.
1.3 Academic Definition Of Marketing
There are many definitions that try to explain what marketing is all about.
This is no easy task either because over the past 20 years, this topic has rapidly evolved.
As it keeps changing makes it hard to determine an concrete depiction.
Lets start with a frequent but older definition.
Marketing institute once described marketing as: “The requirements for being profitable” (Solomon ET AL ,2016, P 9).
Prior to this, the meaning later changed again. They described it as “the strategic business function that creates value by stimulating, facilitating and fulfilling customer demand.”
Since then the definitions keep changing. Dictionary.com explains it is “the action or business of promoting and selling products or services, including market research and advertising.”
The American Marketing Association say it is “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.”
The businessdictionary.com says it is “The management process through which goods and services move from concept to the customer. It includes the coordination of four elements called the 4 P’s of marketing.”
My personal favourite describes marketing as “the way in which an organisation matches it human, financial and physical resources with the wants and needs of its consumers”.
It is a bit of a mouthful, and does not mention those things people usually associate with this subject such as advertising and handing out flyers. This definition does focus on the crucial elements that supports the creation of strategic advertising. This is by how business manage the mechanisms by which relationships are formed between customer and business.
1.4 Academic Definitions Debunked
In 2007, the Institute of Marketing changed their meaning.
This definition was right during this time. But, as business have evolved so as the way we approach customers.
But, why has it changed?
It has changed because as referring to the earlier definition, businesses would do what they could, no matter the costs to sway a purchasing decision.
In hindsight, people were victims of unethical marketing. Being constant victims of fake promises, as their purchases did not meet their promised expectations. The practices were unethical, by which products were forced on people at their most vulnerable.
More recently, people have now stopped responding to the pushy kind advertising.
After all, even to this day, we have all experienced disappointment from spontaneously purchasing from these pushy ads. As a result, we no longer trust this means of marketing.
Studies and statistics now show people are less engaged in those pushy types of commercials: As Forbes (2018), study provides clear evidence. Millennial’s tune out of pushy ads after 5 seconds. This can also explain why people trust Google’s organic listings more over their paid search.
Definitions that are more recent also iterate a similar point.
The focuses on the more recent definitions are about having a good management process:
Firstly, mainly to increase productivity and monitor performance.
Secondly, to manage the value, matching products to the expectations of the customer.
The marketing-mix is a tool that matches product to customer, and what it outlines has to be right in the customers eyes. This includes Price, Place, Promotion and Product.
2. Why Is Marketing Important?
When asked I always say the GREATEST super power is being able to sell anything to anyone!
This is because being able to sell yourself or your ideas is the most powerful skill in the world.
Whether you are applying for a job, business loan, studying at university, or trying to set up a business. Everyone NEEDS to know some basic aspects of marketing.
As peoples demands are constantly changing, it is important to build relationships with people in the market on a personal basis, to learn and deliver a better and more concise value over time.
This means being creative and trying new things.
It is the only way so that they are able to attract people.
If the marketing efforts are persuasive, they will then produce sales. As a result, the business will grow and win an ever-competing environment.
3. The Marketing Infrastructure
The term marketing is an overarching umbrella that includes FOUR main components.
The four components are Brand, Digital, Ethical and Traditional marketing practices.
All must be taken into consideration and each have their own purpose for leveraging a business competitiveness.
3.1 Marketing Infrastructure Model
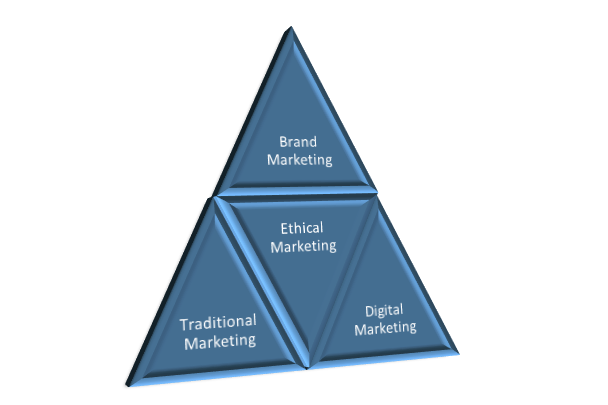
Each one of these components deviates from the scope of this article. However, you can learn about each one of them here…
Every activity you can possibly do is situated under these four components of what marketing is.
4. Marketing Objectives
All marketers must contend with two objectives. These are broken down into:
- Knowing your customers
- Positioning your business
4.1 Knowing Your Customers
The first one is knowing who your customers are by identifying the types of people in the market.
Who Are Your Customers?
This is an investigation of customer age, sex, behaviour and location.
The goal here is to find groups of people that share these similar attributes.
Market research proves to be a vital tool when collecting this information. This is because you can discover finite details of the customer wants and needs.
4.2 Positioning your business
The second one is linking the customer to the brand of the business.
We link the customers through the brand image and corporate messaging.
If the market is competitive, the delivery of the message has to be more precise than the competition. This will increase your chances to beat the competition in that market.
5. Segmentation, Target & Positioning
Through market research, we are able to group a person into their homogeneous similarities, which is segmenting.
Only then by grouping people into their parallel similarities, we can choose which groups are worth targeting.
Marketers evaluate segments to know which customers to target.
To this end, marketers begin to plan how to communicate to this type of person. This is positioning.
Marketers create strategies to communicate with customers.
- Who are the customers?
- Where are the customers?
- What do the customers want?
- How should the customers be approached?
These are rules that answer the above questions.
6. The Marketing Environment
If the product doesn’t meet the expectation of the customer a long term relationship will be difficult to sustain. There are five thing a marketer must consider to sustain this long term relationship with the customer.
6.1 Social and cultural factors
this includes fashion, religion, green issues, equal rights movements.
6.2 Competition
This includes how other businesses in the market solve the problem you aim to solve. This includes direct, indirect and substitute products in the market.
6.3 Technology
New technology advancements are being developed everyday. If your the first to leverage these new technologies you can perform better, and deliver more value than your competition.
6.4 Government and law
This includes political, fiscal, environmental economic and legal. These can affect the profitability and could result in your product not being able in the market. For example, Volkswagen had to recall thousands of its vehicles because the emissions they produced was over the legal limit.
6.5 Institutional changes
a business is always moving in a changing environment and to survive it must change with it. If a business refuses to change it may get left behind.
7. Sales & Marketing
The difference between Sales and Marketing can be identified in a basic marketing funnel. Below is a cycle customers go through from understanding what your business delivers to them making a purchase.
7.1 Where Sales Meets Marketing
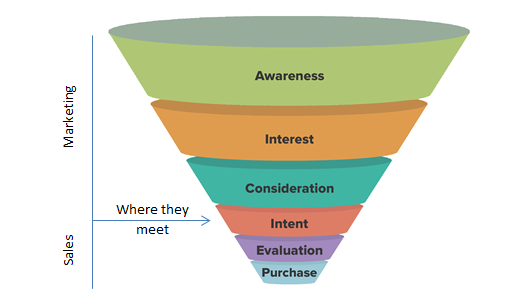
I am not going into detail about what all the elements in the funnel are. But, it is important to note where they meet. In more B2C based companies the marketing department most likely establishes intent with optimised website landing pages and shopping cart/payment ability on the website. However, in B2B it is the sales team that ignite intent through conferences, 1-on-1 discussions and collecting business cards.
More simply, the marketing activities are always the first touch point, whilst the sales team are most frequently the last touch point. However, online businesses can sometimes have marketing take care of all touch points, which works well for some online businesses.
8. Marketing Activities
Marketing activities are broken down into tradition market methods and digital marketing methods.
8.1 Traditional Marketing Activities
The activities that are formed under traditional marketing is all follow a similar means of how we analyse data. This means was less technical and provided less insight to understand how we deliver value to our customers.
Door-to-door marketing
Door-to-door marketing is when salespeople go knocking directly on your house to make sales.
Hand-to-hand marketing
Hand-to-hand marketing is the process of handing flyers or leaflets to prospects on the streets.
Out-of-home marketing
Out-of-home marketing refers to advertising you see on the streets such as banners.
TV Advertising
TV advertising is a means of a promotion utilising the channel of televisions.
Radio Advertising
Radio advertising is a means of a promotion utilising the channel of radios.
Promotional Events
Promotional events are hosting an activity with the end goal of building brand awareness or making sales.
PR and media relations
PR and media relations is managing the reputation of your business through external outlets such as journalists.
Newspapers/ Magazines advertising
Newspapers and magazine advertisement is a means of promoting your/product or service.
Word of mouth marketing (WOM)
This is having people speak about your business. People automatically trust reviews from people they know.
Influencer marketing
Also known as endorsement marketing, is building a brand through having influential people speaking about your brand. This includes people such as celebrities or specialists in the field.
Sponsorship’s
Sponsorship marketing is gaining partnerships and cross-promotion.
Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management is the process to nurture and building trust with your prospects or current customers. Re targeting, is also an effective means for managing relationships in your funnel.
Trade Shows
Trade shows are events to demonstrate your new products or services. Generally, the automobile industry uses these very well.
Seminars
Seminars is another form of event that brings together that have a desire to learn something. This can enable your brand when associated with word wide incidents.
Cold Calling
Cold calling is also known as interruption marketing. This method targets people at their home or business.
Billboards
Billboards display a clear message to increase brand recall.
Flyers
Flyers and leaflets are effective for quick sales or educate the public.
Newspaper
By advertising on newspapers, you can expose your brand to a particular audience to build brand awareness and brand recall.
Telemarketing
Telemarketing is calling people to build a quick relationship via phones.
8.2 Digital Marketing
Technology advancements made the internet possible in the early 1990’s. Because of this we no longer relied on the means to assess data was hands on. Because of digital we could now automate data providing more real time results when building strategies and understand our customer wants and needs.
Content marketing
content marketing involves the creation and sharing of online material (such as videos, blogs, and social media posts) that does not explicitly promote a brand but is intended to stimulate interest in its products or services (Wiki g, 2018).
Email marketing
Email marketing is sending a commercial message, advertisement or promotion through email.
Online newsletters
online newsletters are reports containing information about the activities of a business. This in turn, sends regular notifications to all subscribed members.
Social media marketing
social media marketing is engaging and sharing news, events, and networking through channels such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram and many others.
SEO
SEO is an acronym for search engine optimisation that means tweaking your website so you appear in search engines such as Google and Bing.
Search SEM
Search SEM is paying for traffic on search engines, such as Google Adwords.
Campaigning
A campaign is an agenda that seeks to influence a customer purchasing intent.
Blogging
A blog is journal online, displaying information about a trending topic or issue.
Guest posting
guest posting means writing and publishing an article on someone else’s website or blog.
Affiliate
This is selling someone else’s product through your channels. You act as an intermediary between business and customers. Whereby, you get commission for traffic or sales generated from the referrals.
Webinars
Webinars are seminars but conducted over the internet.
9. The Marketing Dictionary
Below, is the A-Z dictionary of all the terms you need to know to master your role as a marketer.
A.
Aims and objectives
The aims are the result of the marketing efforts. The objectives are the tasks to meet the aims.
Agile Planning
Agile planning refers to a day-by-day plan responding to change agents.
Acquisition
This is process of acquiring new customers.
Analysis
This is the process of gaining insight from data to inform your decision-making.
Analytical tools
Analytical tools are used to help you capture information about your customers which can be later reported on in the KPI’s.
Attractive character
This is a tool that outlines the attributes to build you as an influencer.
B.
Battle cards
These are used by the sales people. They outline how the employers should approach and speak to anyone outside the business. It is a card, with the messaging document condensed into bullet points.
Back end product
This product delivers the main revenue source into the business.
Brand association
This is a form of neuro marketing that begins a connection between something a customer needs with your brand. For example, the apple fruit with mobile phones.
Branding
This is the process to create a name, term, design, symbol, slogan and key messages that people can easily recognised. It distinguishes an organisation or product from its rivals in the eyes of the customer (Wiki c, 2018).
Blue prints
This is a document that consolidation of all the possible paths to get access to your products. It is how they get from first hearing about your offering to the front-end product to the back-end product.
Brand awareness
This is being recognised by people that want to buy your offerings. The aim is for people to recall your brand whenever necessary.
Brand Recall
This is having people being able to recall your brand. The idea is to expose your brand enough to the right people they remember you. By catering your audience regarding certain issues, they will always think of you when they have that problem.
For example, Google is always the first thing you think of when speaking about search engines. On the other hand, when you have a question of some sort, the thought process is to Google it.
Business to business marketing (B2B)
This is also known as B2B. This is when a business sells their products to other businesses.
Business to consumer marketing (B2C)
This is also known as B2C. This is when a business sells their products to specific people.
C.
Cannibalisation
This is when a new product enters into the same market, it may not gain any new market share but eats into the old market share.
Customer journey mapping
This is plotting out the path a customer takes from first hearing about your product to purchase. Engagement – this is the calculable measure of how much people interact with your selling activities.
Concepts
These are ideas how people interact with your business to form strategies.
Conversion
This is when a person does an intended action, that lead to the final purchase or re purchase.
Competition
Direct competition is someone selling the same product/service to the same/similar target audience. Indirect competition is someone selling a substitute product to the same/similar target audience.
Components
These are the parts of the infrastructure, digital, traditional, branding and ethical practices.
Communication
We speak this way to our customers. By knowing the tone and the message that appeal to our target customers, we can cut through the noise of the competition.
Channels
A channel is the means of sending a message to a customer. Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn are examples of social media channels. Promotion – this is reaching out to an audience of people that is attracted to the product, service and brand (wiki a, 2018).
Competitor analysis
This is an assessment of the market eco system. To this end, we can see how well they are performing. This can include outlining out own strengths and weaknesses against the strengths and weaknesses of others in the market. This gives both an offensive and defensive tactics for the future (Wiki d, 2018).
Cultural web
This is a tools used to outline rituals in a business. For the most part, it identifies what the business about; what it does; its mission, its values. This includes all the behaviours of the people (Johnson and Scholes, 1988).
Customer profiling
This is the name given to outline the people that are interested in what you have to sell. This makes it clear whom you are targeting in your key message.
D.
Digital marketing
This is working with using channels Such as, search engines, websites, social media, email, and mobile apps (market, 2018).
Direction
A marketing direction is a yearly plan broken down to meet the marketing aims.
E.
Envision
Envisions always change as time changes. Envision, or envisioning is regular fine-tuning of the overall vision responding to change agents.
Ethical marketing
This is working with a moral sense of value.
External analysis
This is an assessment of the wider business environment. This is outlining things that are out of your control, which could affect the future of your business, such as competition.
F.
Funnels
This is a plan used to filter people from the front-end product to the back-end product.
Five forces
This is a tool used to assess the competitive landscape.
Front-end product
This is a product that delivers a high amount of value and it leads customers to the back end product.
G.
Gap analysis
There are three parts to a gap analysis. Firstly, it evaluates your current performance. Secondly, it looks at the potential in the market. Thirdly, it makes a premise of other areas our business in missing in the market. Largely, it brings forwards the potential rewards in the market.
H.
Hooks
This s a proven way to catch a person’s attention – they entice a customer to purchase a product. Other hooks arouse interest in a product or service to elicit further interaction for the future.
I.
Ideal customer model
This is creating an avatar of your best customer. In order to build a visual we estimate what they would look like and how they behave.
In bound marketing
This uses the pull method to bring people to your products and services. This means us not forcing your audience to purchase. It consists of content and social media marketing. Search engine optimisation and branding (Wiki b, 2018).
Industry
An industry is the production of goods and services within a market.
Influencer marketing
This is building a domain of authority through a good perceived reputation in the industry.
Industrial analysis
This is what we do to assess the competing forces in the market (Corporate Financial Institute, 2018).
Internal Analysis
This is assessing how well a business turns raw materials into the final product. It assesses the operation to the amount of value delivered in the value chain.
K.
K
Key performance indicator (KPI)
This is assessing and measuring whether we are on track to hit the aims. We quantify our outputs against our objectives.
Know like and trust
Know Like and Trust is the mental process a person goes through from being a lead to a potential customer. When a person trusts you, they are likely to buy something from you, and refer you to friends whom will become customers. A person must go through these three phases and having trust will provide purchasing intent and word-of-mouth marketing.
L.
Leads
Also known as acquisition, leads are people that have shown a want or need for your product or service.
Lead generation
This is outlining all the channels your customers come from, and creating strategies to increase the volume of people entering your business.
Level of strategy model
this is splitting a marketing plan into three key areas. In any event, it helps to split your operations into three areas. This is for having a productive management system. There is corporate level, functional level and operational level. The level of the strategy is a good way to know which area of the business is responsible for the on-going tasks. Having focused roles deliver the best outcome.
M.
Market
A market is a group of people that all share the same problems and have the same interest.
Marketing Machine
This is a tool that plans the scope and activities at the operational level.
Marketing Mix
This is a summary of the product. Through the four P’s (price, promotion, product and place), it is a guideline how to deliver the product to the market.
Market Research
This is investigating the types of people in the market, and there wants and needs.
Market share
Is the fraction of the people that bought a product in the market. Methodology – This process reveals a systematic plan to perform the daily operation. Following this will increase productivity and increase the chances for better results.
MICRO
These are the elements within business day-to-day tasks. Looking in detail how we perform our tasks can result in being able to improve this and increase efficiency (business dictionary b, 2018).
MACRO
These are the tools used to assess the parts outside of the business. We do not have full control over these factors, and so there must be a careful decision making process to mitigate any foreseen problems. PESTLE is a known tool to conduct the analysis.
N.
Niche marketing
a niche is a very narrow customer segment that has really specific goals. This means outlining who the people are in that niche, and then get a very finely tuned message to them – the more specific the message the better the sale rate.
Neuro marketing
this is referring to the psychological reflections of a customer. Neuro marketing is techniques built into the customer journey and brand. Done correctly can influence the way people think and interact with your product and serves.
Nurture
Nurture is the method to develop long lasting relationships with buyers. A good nurturing program will look at details at every stage of the sales funnel. It is having a focused communication effort, listening to the needs of the prospects. Being able to focus your communication will provide information that is more meaningful to people; this will increase the value you will offer (Market b, 2018).
Naming conventions
These are compelling descriptions of a product/service.
O.
Out bound marketing
This is a traditional marketing method known as interruption marketing. It uses the push method, which can sometimes mistakenly force your products/services on people that do not want them. This includes activities such as trade shows, seminar series, and cold calling.
P.
Persona
This is creating an avatar so that we have a visual reference of the target customer.
Positioning
This is a continuation of the targeting phase. This is the message that we believe fit for making sales. By asking the question: What does our target customer want to hear? So, that they remember and value our business.
Process
This is the plan to order the objectives in a streamline way to reach the marketing aims.
Plan
A plan is a detailed proposal for reaching the aims and objectives. It usually has a breakdown of the entire task, with the amount of time to complete each task.
Polarising effect
This is how people react to your target message. People will react in good ways and bad ways. It is important to note whatever position you take, as groups of people will both love you and hate you. It is very critical to outline the polarisation of people when considering your positioning path.
Product
A product is a tangible offering to your customer. This is something you physically touch it touch. Like food, cars and mobile phones.
Product life cycle
This is the life expectancy of your products and services. When a product is new to the market, it will remain popular for a certain length of time. After some time, it will later die off.
Purchasing intent
This is what the customer aims are when they use your product and service.
PESTLE
This is a tool that can analyse different the external parts of the business. It covers six metrics. The first is the politics in a given area. The second is assessing the environment you are in, that includes things like weather conditions and anything geographic. The third can include social treads. The fourth is technology, and how it can increase your game. The fifth is legal; outlining what laws can cause barriers. The sixth is assessing the economic climate (Business dictionary, 2018).
Perceptual map
This is a tool that visually represents how you position against your competitors in the market.
Positioning statement
This identifies clearly of the justified positioning strategy.
R.
Re targeting
This is putting a plan in place to get a prospect to shop again and make another purchase. This can also include going after people that you failed to convert the first time around.
ROI
ROI means return on investment. It works out the margin between the costs and the selling price of a product.
S.
Stakeholder matrix
Assesses who has the influence and power. It outlines which people can effect change in your business. A good assessment breaks down the interests of these people (Wiki f, 2018).
Service
A service is defined as a not a tangible offering to your customer. This means it is not something you cannot touch. Like waiters at a restaurant and mechanics at a garage.
Segmentation
This is the process of putting people into groups, based on their similar qualities. By putting people into groups, you can visualise what the market looks like, and how to approach it. Strategy – this is a set of tasks created to fulfil the objectives. The strategy is guidelines that we use to reach the business.
SMART GOALS
This is a way to assess where your business is going. When you have an idea of your direction, this tool can help you focus how to get there. SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time.
SWOT
This tool evaluates your overall performance in the market. It means Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Treats.
Segmenting dimensions
This is a model that covers all the ways people can be grouped. The four most commonly seen are Geographic, Demographic, and Psycho graphic and behavioural.
Segment scoring
This is score given to outline what customer group is worth your effort.
Soap opera sequence
These are the hooks to catch people’s attention when creating a story for your brand.
T.
Targeting
This is a continuation of the segmentation phase. It is evaluating which people we focus on.
The Customer
A customer is a person that has made a purchase from your business.
The Customers experience
A feeling customers have when they go through your purchasing process.
The Customers journey
This is the process a person goes through from first hearing about your product to making a purchase this process. Reverse engineering in the technique used to do this. This means you start with the end purchase a work your way back to the lead generating activity.
Traditional marketing
This is the first form of marketing before digital. This includes approaching customers face to face and over analogue channels such as the TV.
V.
Value
Value is the list of the perceived benefits. This is a person’s experience from lead to sale, and the benefits of the product. If the benefits outweigh the inconveniences, then the product and service has a perceived level of value. Value chain – A value chain used to describe how to transform raw
Materials into a finished product.
VIRO analysis
This is a tool to assesses the businesses resources and labour skills.
Value proposition
0this is a statement that outlines why a person would want to buy your product or service. As a result, it is very useful to align employers.
Vision
Vision is the end picture you wish to be for the greatest success in that period.
VMOSA
This is a way to plan the direction. This tool defines a vision and enacts change (CTB, 2018). It stands for Vision, Mission, Objectives, Strategies, and Action Plans.
W.
Wants and needs
Wants and needs refer to the view of value within your product. Wants refers to a personal desire whilst a need refers to a necessity. For example, people want the comfort of their own vehicle, yet they need fuel. Knowing this, marketing towards the wants… i.e. the comfort of driving will be a more successful marketing campaign.